AI synthesize
AI synthesize can be especially useful in the following situations:
To generate synthetic feature dataset for ML model development.
When statistical accuracy and maximum privacy are needed.
To expand dataset rows while maintaining original statistical properties.
Apply AI synthesize
Open your workspace.
From the Main hub or Table view tab, select the column where you want to apply a generator.
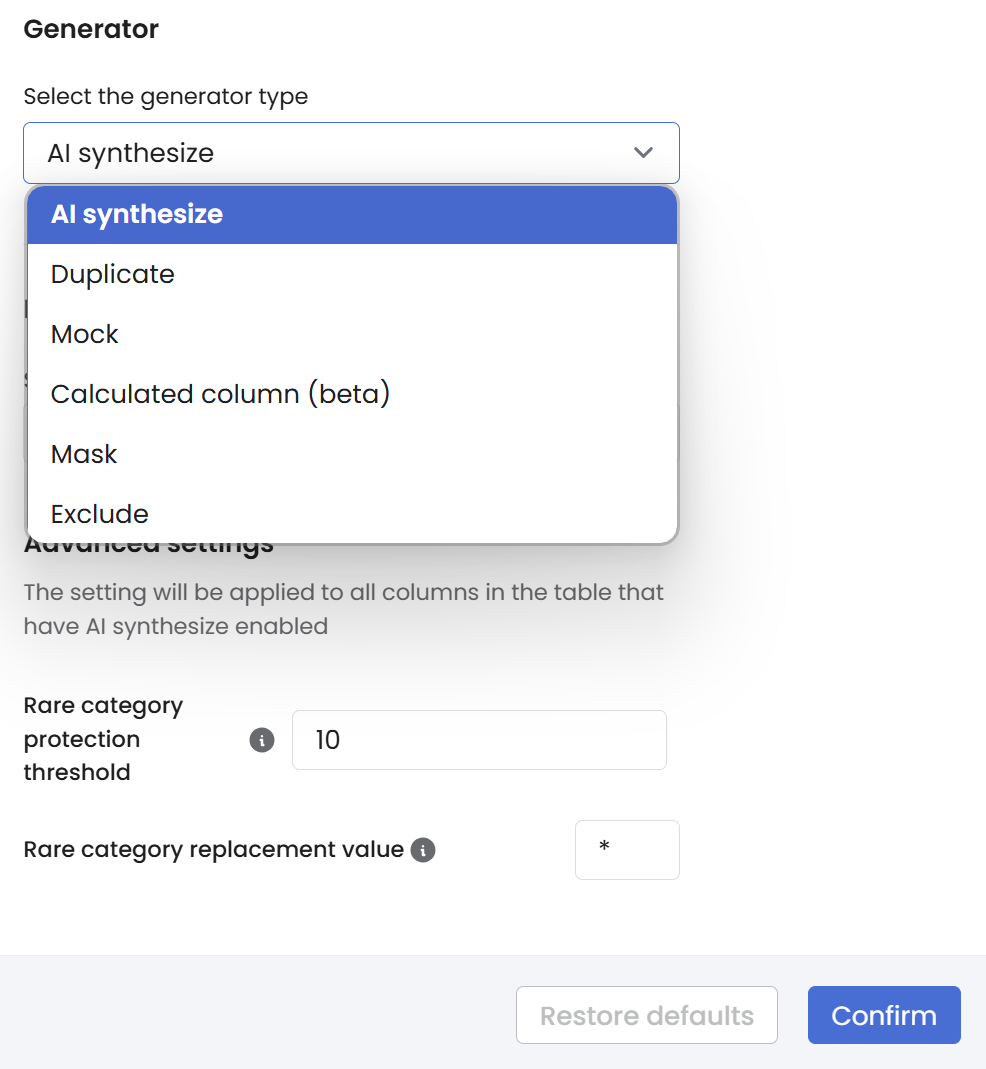
Under Column parameters > Generator, select AI synthesize to enable Syntho's machine learning (ML) models to automatically synthesize the data in your tables.
Set the relevant AI synthesize parameters.
Select Confirm.
Preparing your data
When using AI-powered synthetic data generation, it is important that your data is fit to synthesize.
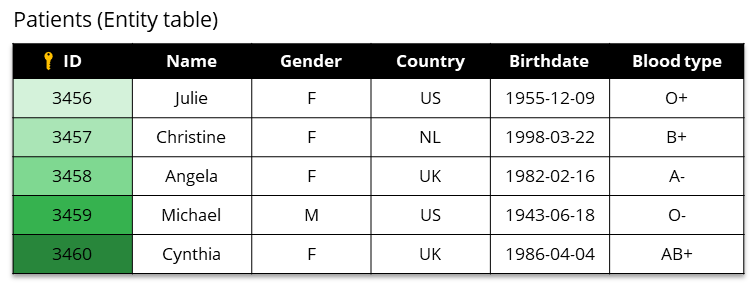
Entity tables
Syntho expects your data to be stored in entity tables that satisfy the following:
To minimize privacy risks and improve the training algorithm's generalization ability, as a rule of thumb, a minimum column-to-row ratio of 1:500 is recommended. For example, if your source table has 6 columns, it should contain a minimum of 3000 rows.
Each entity is described in one row.
Each row can be treated independently. The order of the rows does not convey any information. The contents of one row also do not affect other rows.
Avoid column names with privacy-sensitive information, like
patient_a_medications,patient_b_medications, etc.. Instead, have a patient column with the names. This prevents patient names from being exposed in metadata or bypass rare category protection (e.g., there’s apatient_acolumn, but this patient only appeared five times in the whole dataset).Remove columns that are derived directly from other columns. For example, you may have a
net_amountcolumn that is derived from thegross_amountandtaxescolumns. For categorical columns, there could be hierarchical relationships, such as a redundantTreatment categorycolumn referring to aTreatmentcolumn. Removing such redundant columns will simplify the modeling process and will lead to higher quality synthetic data.
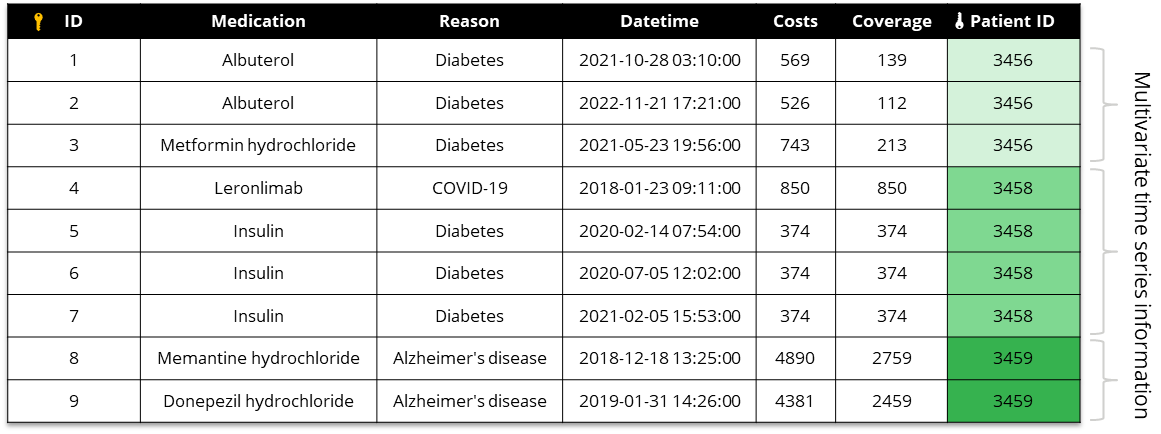
Entity table-linked table dataset
Syntho is capable of processing data in the form of lists, sequences, or time series when structured in entity table-linked table structure. Ensure your data satisfies the following:
The structure is tailored for handling lists, sequences, or time-series data.
It includes two tables:
an entity table that satisfies the Entity tables requirements.
a linked table.
Each record in the entity table needs a unique ID (primary key).
Each record in the linked table must reference the unique ID from the entity table (foreign key).
Similar to the requirements for Entity tables, eliminate columns whose values are directly derived from other columns.
Remove row values that are derived directly from values in other rows. For instance, if your dataset includes sequences with
start_dateandend_datecolumns, and eachstart_datematches theend_dateof the row before it, remove one of these redundant values, understart_dateorend_date.For more information on preparing your data when synthesizing complex table relationships see: Sequence model.
Supported data types
The Syntho platform supports a wide variety of data types. Under the hood, Syntho uses an encoding scheme where each data type is mapped to one of the following encoding types.
Numerical counts (e.g. number of visits)
Continuous values (e.g. weight, temperature)
Predefined values (e.g. blood type, country)
Timestamps and dates (e.g. created at)
Discrete
Syntho uses a discrete encoding type to synthesize numerical values that have a countable number of values between any two values. For example, the number of customer complaints or the number of flaws or defects.
Continuous
To synthesize numerical values that have an infinite number of values between any two values, such as weight and height, Syntho uses a continuous encoding type.
Categorical
A categorical column has one of a fixed number of possible values. These variables, like the blood type of a person (i.e., A, B, AB or O), have a fixed set of categories. Categorical encoding prevents random values (for instance, M, X or Z) from appearing in your synthetic dataset.
Under the Encoding type > Advanced settings, the Rare category protection settings will appear, which can be used to protect rare categories. These categories could potentially re-identify outliers within the synthetic data.
Note: The categorical encoding type is the default fallback encoding type used by Syntho. This means that any database types that are unknown by Syntho will automatically be encoded as categorical.
Datetime
The encoding type known as Datetime is used to describe values that incorporate either one of, or both a date component and a time component.
By using this encoding type, Syntho is able to synthesize these values and generate dates and times that are statistically valid and representative.
Syntho supports all date and datetime data types for the Syntho connectors.
Limitations
Datetime columns support precision up to milliseconds. Nanosecond precision is not supported.
Rare category protection
Following the privacy-by-design principle, Syntho automatically replaces all rare categorical observations with a user-defined value in a column encoded as a categorical column.
Replacing those rare categories helps to prevent that those sensitive values leak through into the synthetic data.
Rare category protection threshold: All column values that occur as frequently or less than the rare category protection threshold are automatically replaced.
Rare category replacement value: All column values that occur as frequently or less than the rare category protection threshold are automatically replaced by this replacement value.
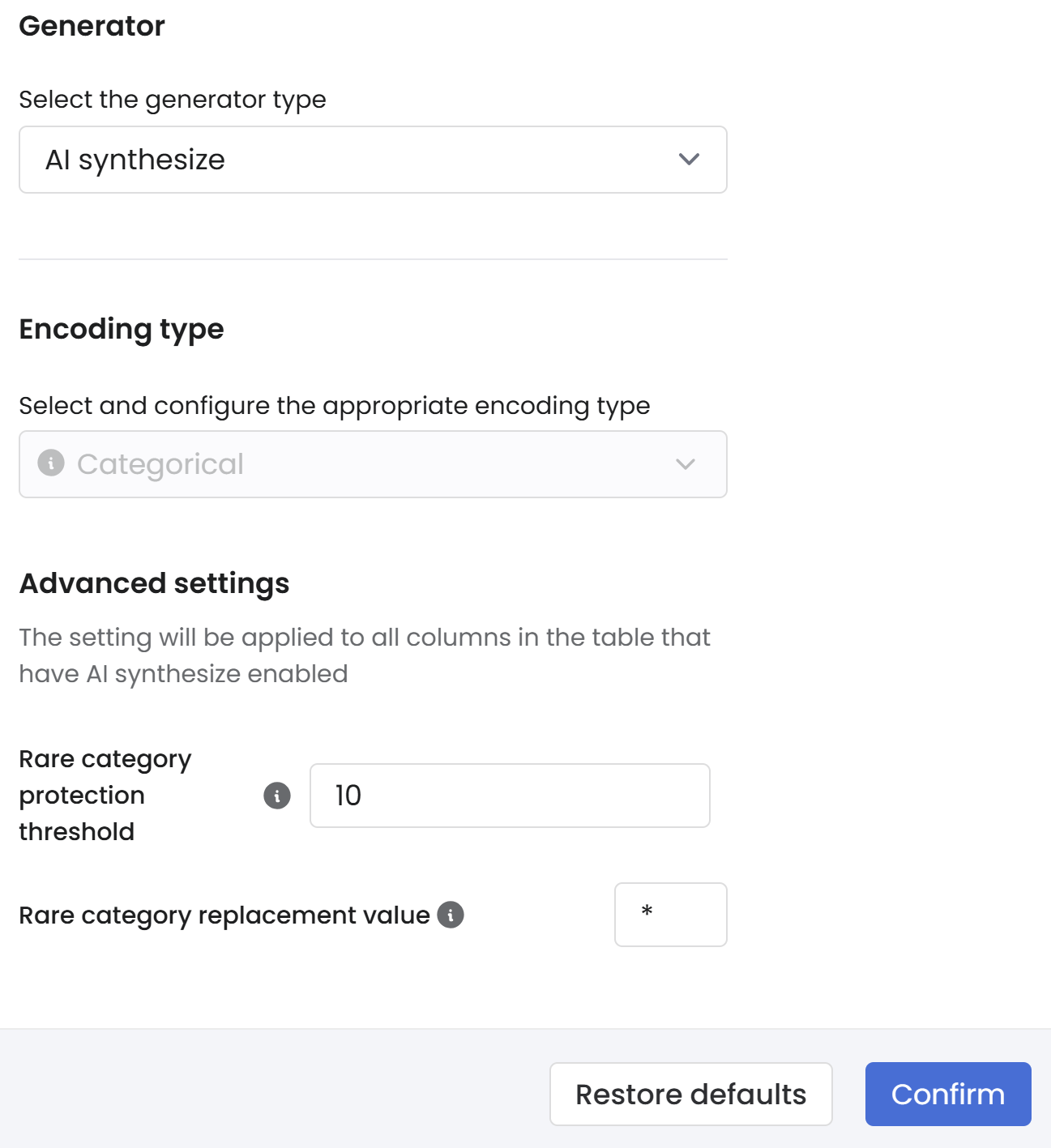
Under Column parameters > Encoding type, select Advanced settings to adjust the Rare category protection threshold and Rare category replacement value.
By default, the rare category protection threshold value is set at 10. This means that all column values that occur 10 times or less are automatically replaced by the user-defined value.
Under Column settings > Encoding type, select Advanced settings to adjust the Rare category replacement value.
By default, the rare category replacement value is an asterisk (*). This means that all values that occur equal or fewer times than the rare category protection threshold value will be replaced with the replacement value.
Advanced settings
Advanced generator settings
Go to Table settings on the right panel, scroll down to see Advanced settings to view and adjust settings on the generator-level. Depending on the job configuration, a generator is applied to one or more columns.
You can adjust the following advanced generator settings:
Maximum rows used for training: The maximum number of rows to be used for training. Using fewer rows can speed up the process. Leave this value at None to use all rows for training.
Take random sample:
On: takes a random sample of rows used for training.
Off: takes the top rows as defined in the database.
Advanced column settings
Select Advanced settings under Encoding type to view and adjust settings on the column-level.
You can adjust the following advanced column settings, depending on the selected encoding type:
Discrete | Continuous | Datetime
Clipping threshold: The floor and ceiling of a column as the
Nthlowest and highest value, whereNis the clipping threshold. The threshold value will process the values as not to exceed the ceiling and floor.
Categorical | Text containing PII
Rare category protection threshold: All column values that occur as frequently or less than the rare category protection threshold are automatically replaced.
Rare category replacement value: All column values that occur as frequently or less than the rare category protection threshold are automatically replaced by this replacement value.
Locale: The locale used by the text processing models for columns with text containing PII.
Was this helpful?

