Numeric (integer)
Below is a list of available numeric (integer) mask functions.
Hasher
The Hasher function uses the Hasty Pudding Cipher algorithm to create a one-to-one mapping between input and hashed values, ensuring consistent anonymization. It maintains the sign of numbers, always hashing negative values to negative outputs and positive values to positive outputs, using an internal encoding mechanism. This method ensures stable, deterministic, and repeatable transformations, making it ideal for anonymization while preserving numerical relationships. To ensure accurate ordering, please see ordering and indexing considerations.
Parameters
No parameters.
Note: The default fallback range aligns with 32-bit integer limits (-2,147,486,647 to 2,147,486,647), though actual range depends on database support. Note that 0 is never hashed.
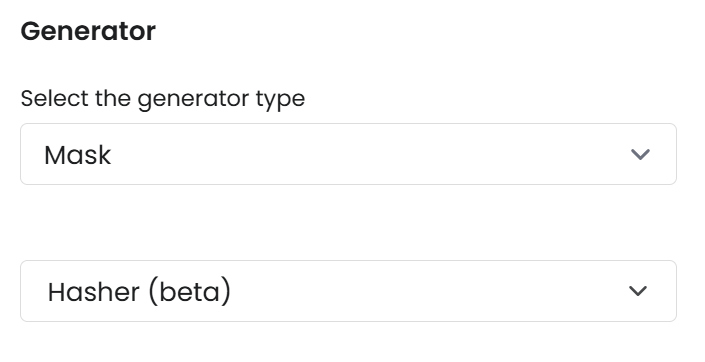
Example
If you configure:
Column names:
2002,
1944,
2002,
...The results will be:
Column names:
1962697134,
943111608,
1962697134,
...
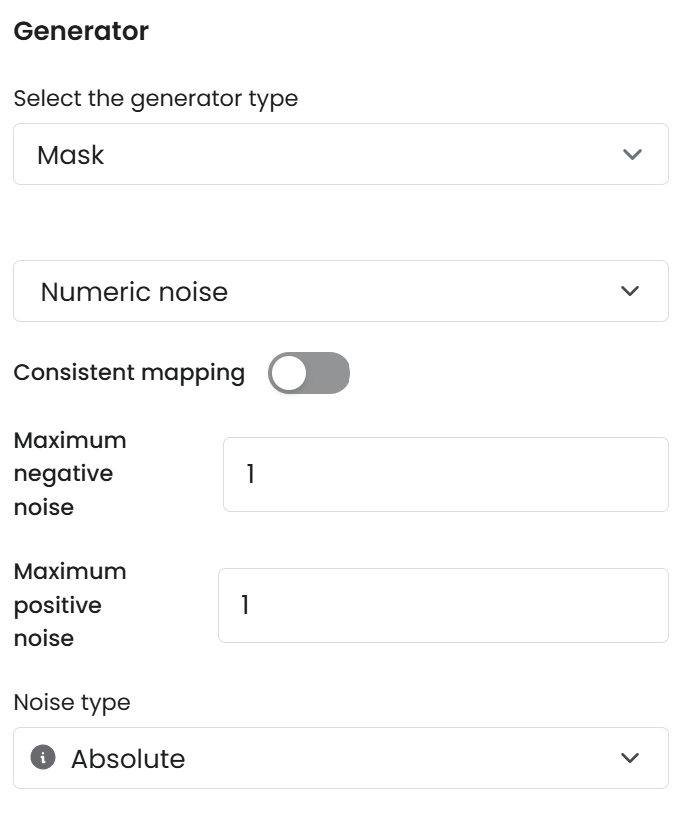
Numeric Noise
Adds noise to numeric data based on a uniform distribution, ensuring that the values are randomized while preserving the overall structure of the dataset. This is useful for anonymizing numerical fields where consistency and distribution must be maintained.
Parameters
Maximum negative noise: The smallest amount the date can be adjusted, relative to the original date.Maximum positive noise: The largest amount by which the date can be adjusted from the original value.Noise type: The unit of time (Additive, Multiplicative, Absolute) that will define the granularity of the shift.Additive: Syntho adds random noise sampled from a range between –x% and +x% of the absolute value. For example, with a 10% max negative and positive noise percentage, and value 20, noise is sampled from –2 (inclusive) to 2 (exclusive).
Multiplicative: Syntho multiplies the value by a random factor between the specified Min (inclusive) and Max (exclusive). For example, with values -5 and 5, values are multiplied by a factor between -5 and 5.
Absolute: Adds random noise directly to the value, within the specified fixed range (e.g., –5 to 5).
Consistent mapping: Numeric Noise supports consistent mapping.
Example
If you configure:
The results may be:
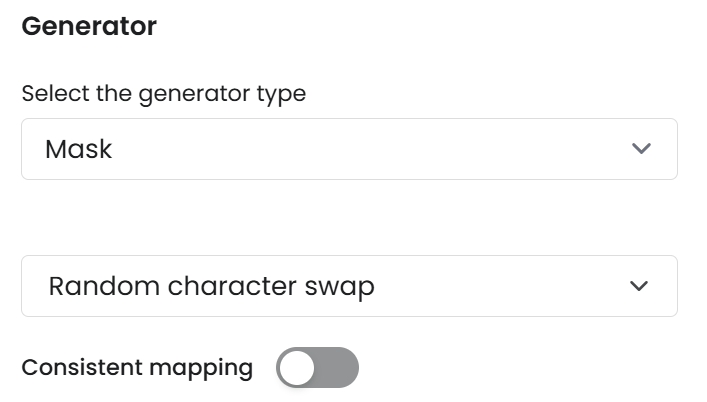
Random Character Swap
The Random Character Swap function replaces individual characters in categorical values while preserving the structure of punctuation, spaces, and symbols. Characters are swapped within their respective categories (letters with letters, digits with digits), ensuring that the field's overall format remains usable, or in other words, the original data type and structure of each field (letters, numbers, symbols) are preserved. Note that it preserves non-alphabetic characters (e.g., punctuation, spaces).
Parameters
Consistent mapping: Random Character Swap supports consistent mapping.
Example
If you configure:
The results will be:
Was this helpful?

