Sequence model
Note: Before using this feature, make sure your data is set up as described in the Prepare your sequence data section.
Syntho is capable of processing data in the form of lists, sequences, or time-series when structured in entity table-linked table structure.
Syntho's synthetic data sequence models allows you to capture relational information between any entity table and linked table. Entity tables contain the profiles of data entities, while linked tables reference them.
Entity tables can be identified by their attributes, which describe privacy-sensitive information about data entities, such as names, birthdates, phone numbers, addresses, and more. Linked tables often contain event information about a referenced entity, which can span multiple rows per entity, such as a monthly salary payment.
Let's consider the Patients and PatientMedications tables shown below. Here, the Patients table is the entity table. The PatientMedications tables is the linked table.
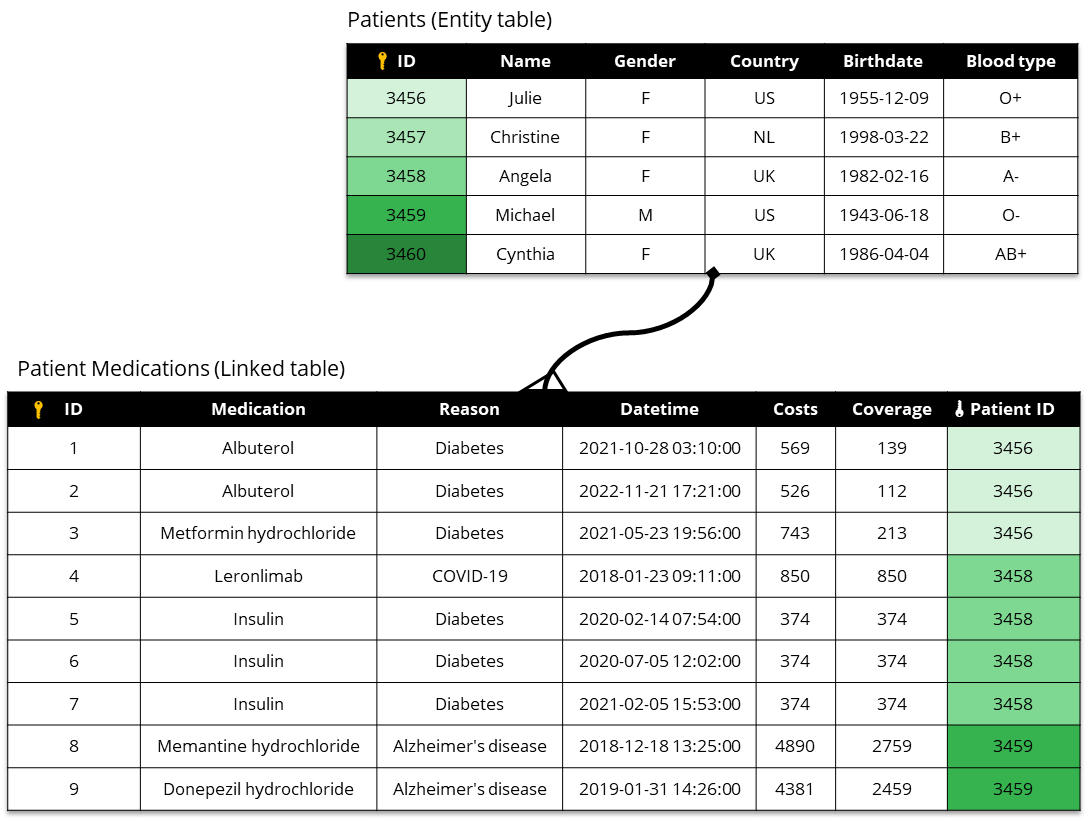
To synthesize these tables using Syntho's sequence models:
Syntho starts by synthesizing the
Patientstable.Then, it synthesizes the
PatientMedicationstable using the synthetic Patients table as context.
How to apply Syntho's synthetic data sequence model
To use Syntho's synthetic data sequence models, you can do the following:
On the Table view tab, enable the Enable sequence modeling.
Finally, select Start generating.
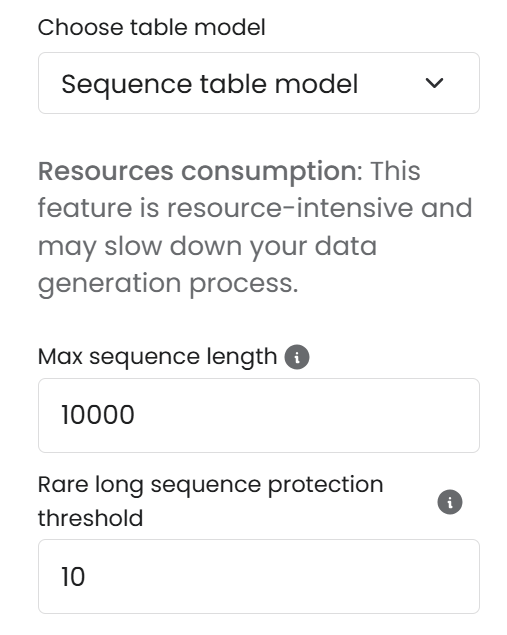
Sequence model parameters
Before initiating the generation process, you have the option to modify sequence model parameters. Here's an overview:
Max sequence length: Sets a cap on sequence lengths, truncating any sequence that exceeds this limit.
Rare long sequence protection threshold: Defines a limit for the length of data sequences used in training, adjusting the longest sequences to the length of the Nth sequence.
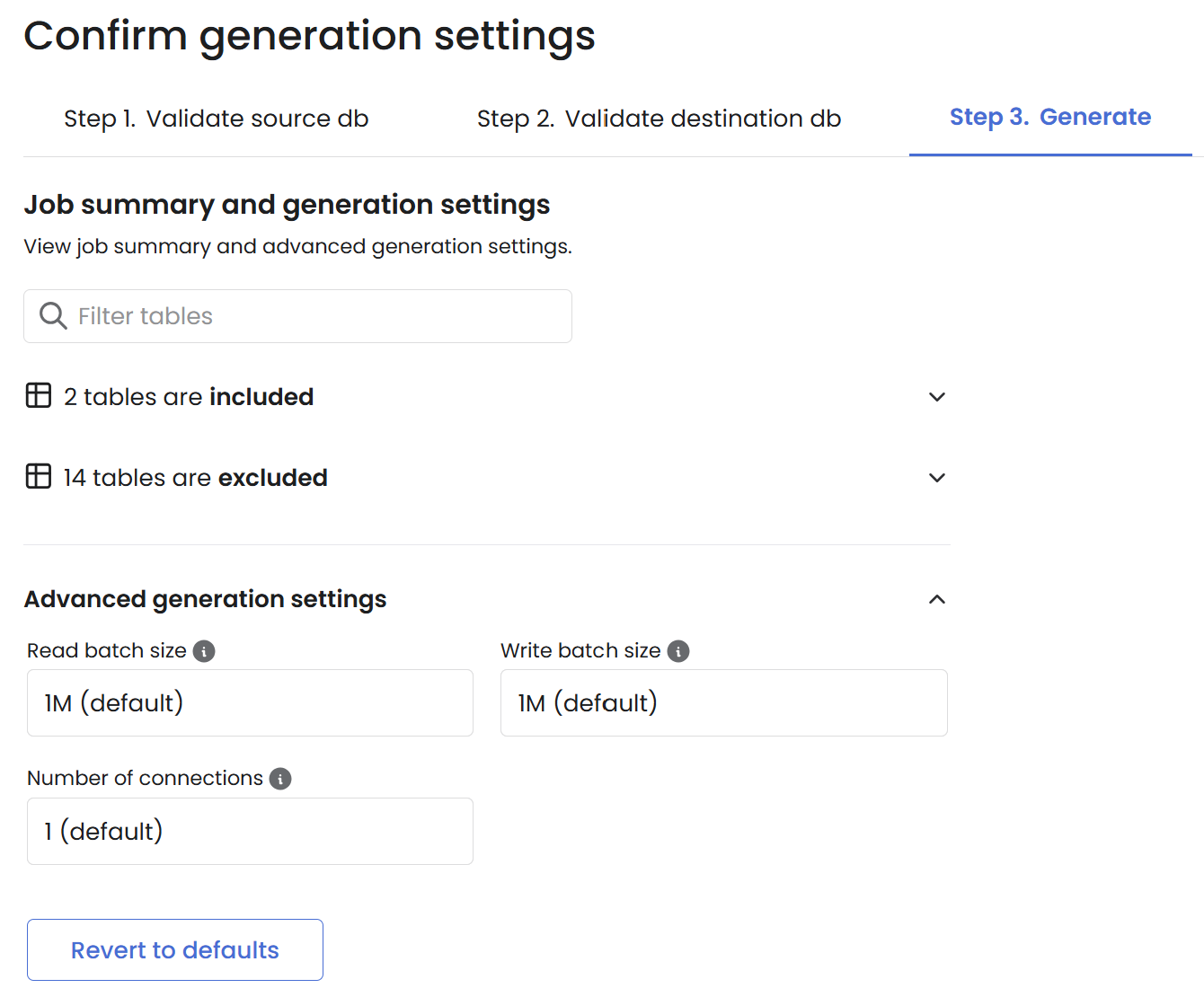
Read batch size: The quantity of rows read from each source table per batch.
Write batch size: The quantity of rows inserted into each destination table per batch.
N connections: Specifies the number of connections.
Limitations & Recommendations
It is important to consider the following when using Syntho's sequence models:
2 tables: Syntho has limited the use of its sequence models to 2 tables that are structured according to the entity table-linked structure to maximize the synthetic data utility.
Order of rows: For your linked table, it is recommended to store the rows in the correct order. This information will be used to train Syntho's generative AI models, so it can leader to higher quality synthetic data. The ensure reading order preserved, ensure a primary key or index is present in the linked table.
Resource Consumption: This feature is resource-intensive and may slow down your data generation process. Consider reducing your input data or adjust the sequence model parameters to reduce time and resources for your job.
Last updated
Was this helpful?

