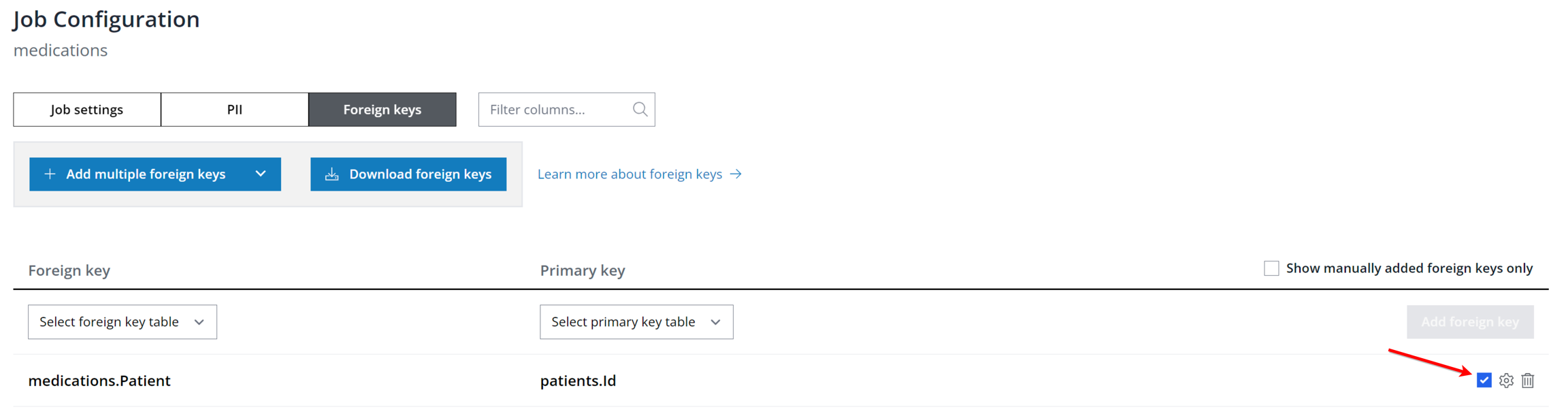
Import foreign keys via JSON
[
{
"apply":true,
"fk_columns":[
"FK_COLUMN_NAME"
],
"fk_schema":"FK_SCHEMA_NAME",
"fk_table":"FK_TABLE_NAME",
"pk_columns":[
"PK_COLUMN_NAME"
],
"pk_schema":"PK_SCHEMA_NAME",
"pk_table":"PK_TABLE_NAME"
},
{
"apply":true,
"fk_columns":[
"FK_COLUMN_NAME"
],
"fk_schema":"FK_SCHEMA_NAME",
"fk_table":"FK_TABLE_NAME",
"pk_columns":[
"PK_COLUMN_NAME"
],
"pk_schema":"PK_SCHEMA_NAME",
"pk_table":"PK_TABLE_NAME"
}
]
Was this helpful?

