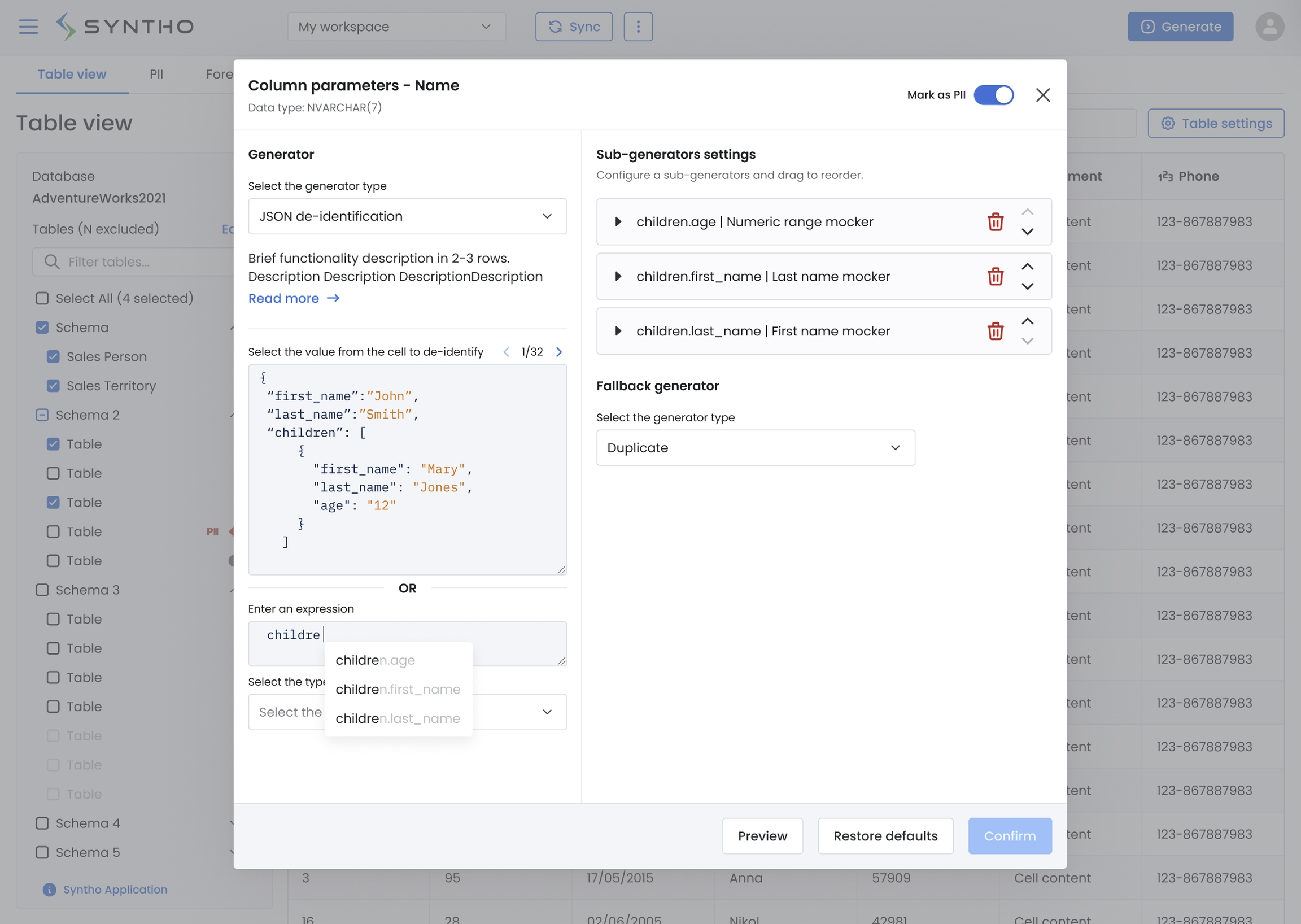
JSON de-identification
Coming Soon
The JSON de-identification feature allows users to apply targeted masking to specific sub-values within complex JSON structures. This feature enables precise and flexible data de-identification based on user-defined JSONPath expressions, helping users efficiently manage sensitive data in nested JSON structures. Below is an overview of how to use this feature, followed by detailed instructions.
Apply a JSON de-identification
Open your Workspace.
From the Main hub or Table view tab, select the column where you want to apply a generator.
Under Generator, select JSON de-identification.
Either:
Select the value from the cell to de-identify (The expression input field will then be populated based on this selection), or
Enter a JSONPath expression to specify which sub-values within the JSON structure the generator should target.
Assign Sub-Generators:
In the Sub-generators settings panel, configure each sub-generator based on the specific attributes you wish to mask. Available generators in sub-generators are Duplicate, Mocker, Calculated Columns, Mask, Exclude.
For instance, apply a numeric range mocker to
children.age, a first name mocker tochildren.first_name, and a last name mocker tochildren.last_name.Sub-generators are applied in the order they appear in the list; you can reorder them as needed by dragging each item.
Configure Fallback generator:
Select a fallback generator from the dropdown menu to apply to values that do not match the defined JSONPath criteria or result in errors. The default option is Duplicate and the other option is Exclude.
Filter by JSON type (Optional):
To increase specificity, you can restrict the generator application to particular JSON primitive types (i.e. Number, String, Boolean and Null) to match the data structure requirements.
Save and Preview:
After configuring the JSONPath expressions, sub-generators, and fallback options, click Preview to view how the de-identified data will look.
Once satisfied, click Confirm to save the settings.
JSON de-identification parameters
JSON de-identification supports selective application of generators to sub-values within JSON data. Users can define complex criteria, such as JSONPath expressions, to target specific elements within JSON arrays and objects. This functionality ensures accurate data masking while preserving the structural integrity of the JSON data.
Sub-generators settings: Define multiple sub-generators and apply them sequentially to sub-values based on JSONPath expressions.
Fallback generator: Specify a fallback generator to handle values that cannot be masked by the main generator due to errors or mismatches.
Expression validation: When a JSONPath expression is entered, users can validate it to see how many JSON elements match the criteria.
Filtering by data type: Restrict generator application to specific JSON types (e.g., string, number) to ensure relevance and efficiency.
Was this helpful?

