Single Sign-On (SSO) in Azure
Introduction
Kubernetes (Helm chart)
backend:
env:
SSO_PROVIDER: Azure
SSO_CLIENT_ID: <your-client-id>
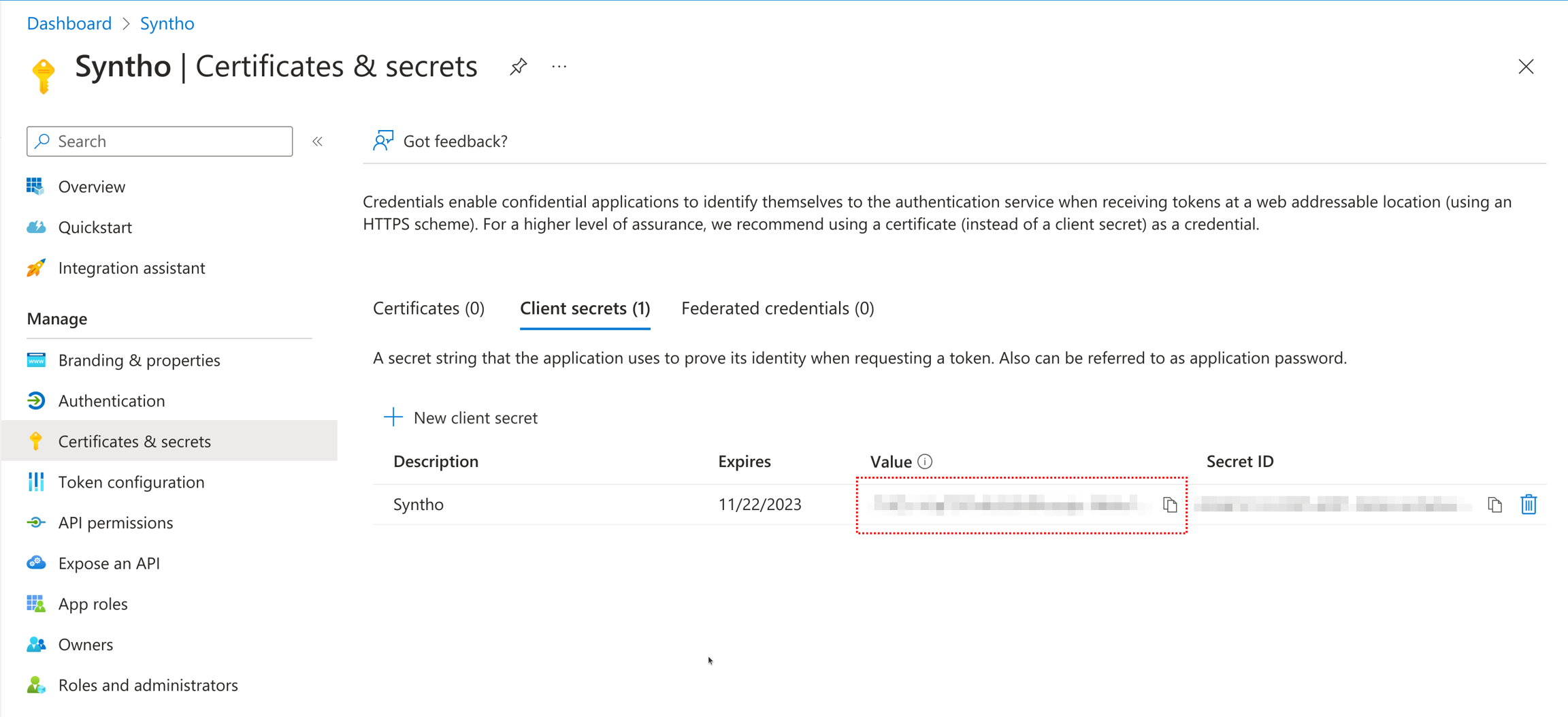
SSO_CLIENT_SECRET: <your-client-secret>
SSO_TENANT_ID: <Azure tenant-id>
USERNAME_PASSWORD_LOGIN_ENABLED: TrueDocker Compose
version: '3'
services:
backend:
image: ${BACKEND_IMAGE}
restart: on-failure
environment:
...
SSO_PROVIDER: Azure
SSO_CLIENT_ID: <your-client-id>
SSO_CLIENT_SECRET: <your-client-secret>
SSO_TENANT_ID: <Azure tenant-id>
USERNAME_PASSWORD_LOGIN_ENABLED: "True"Username and password login
Single Sign-On
OpenID Connect
Azure
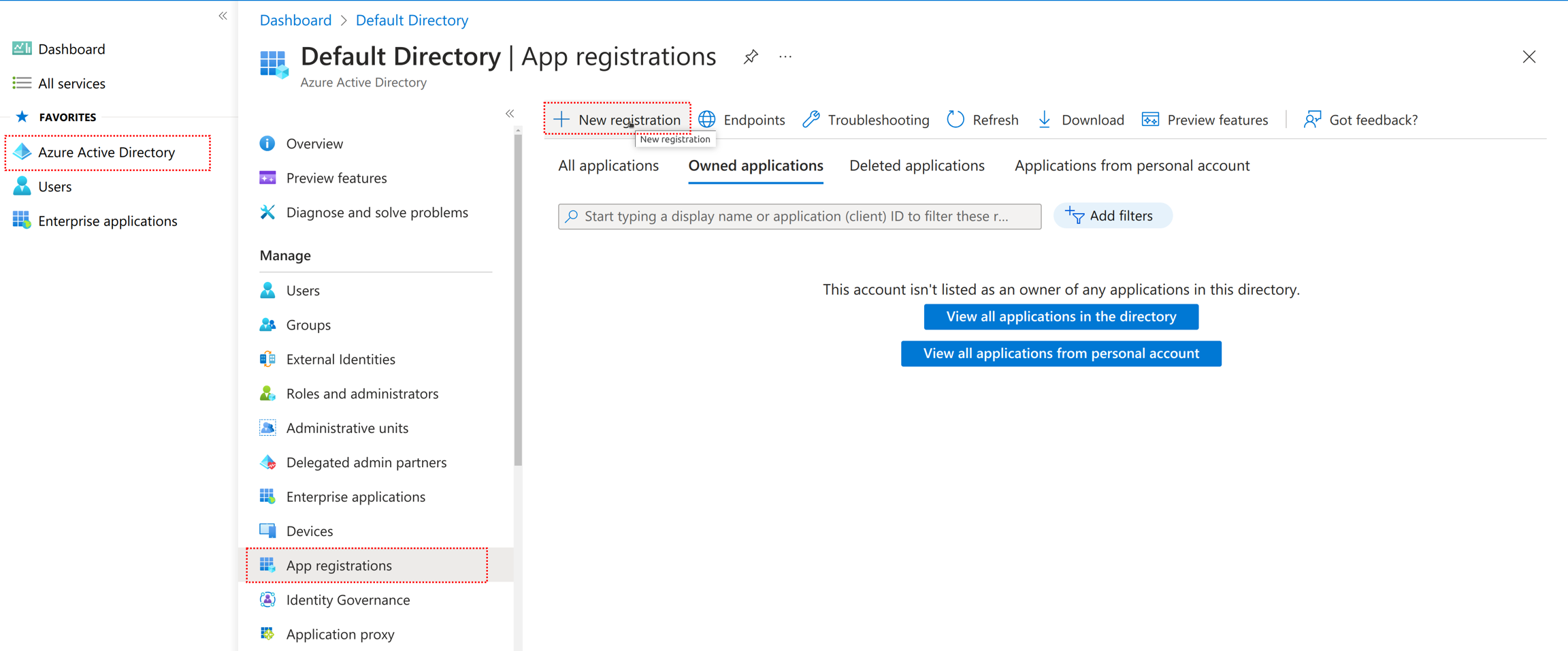
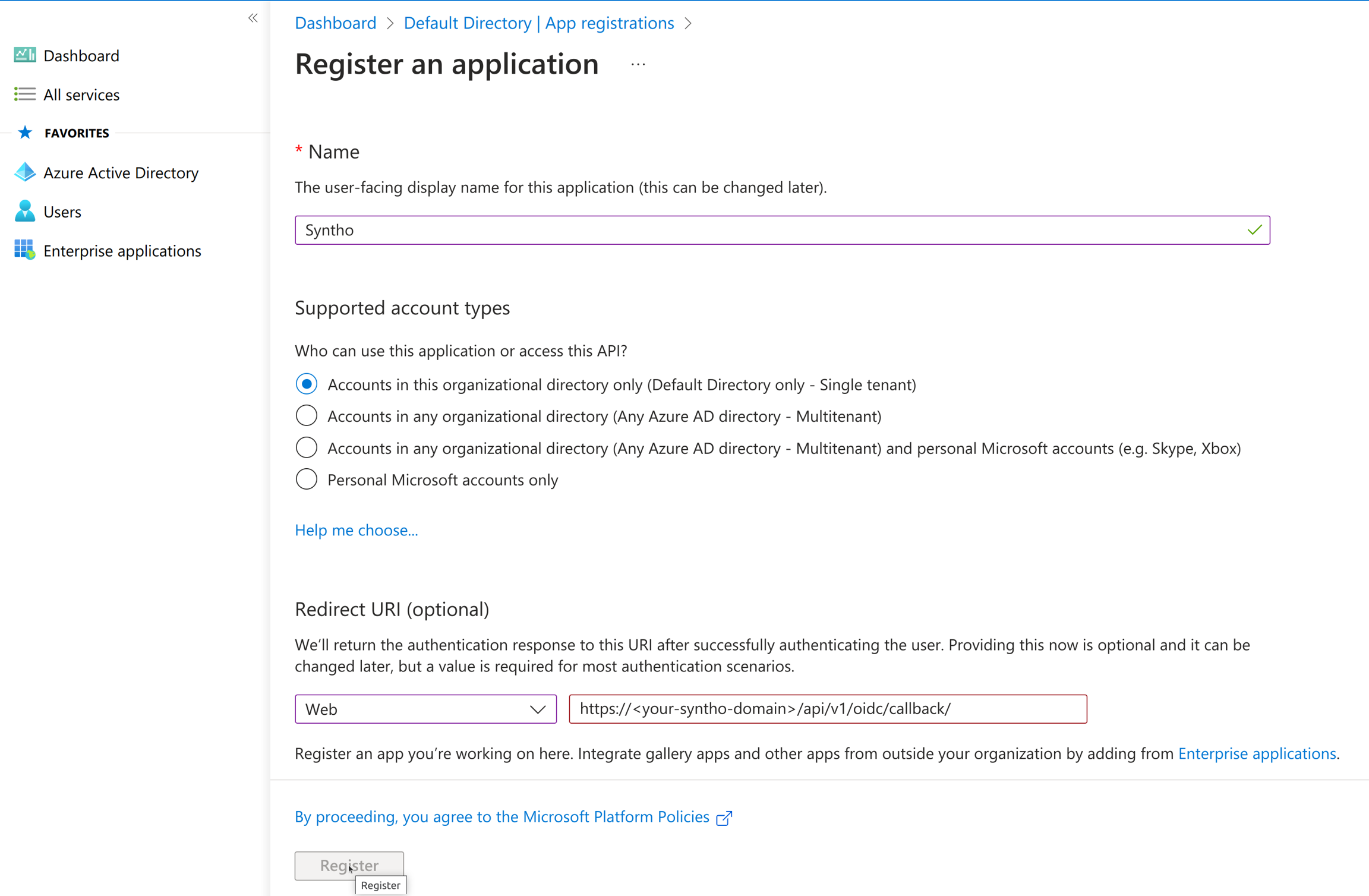
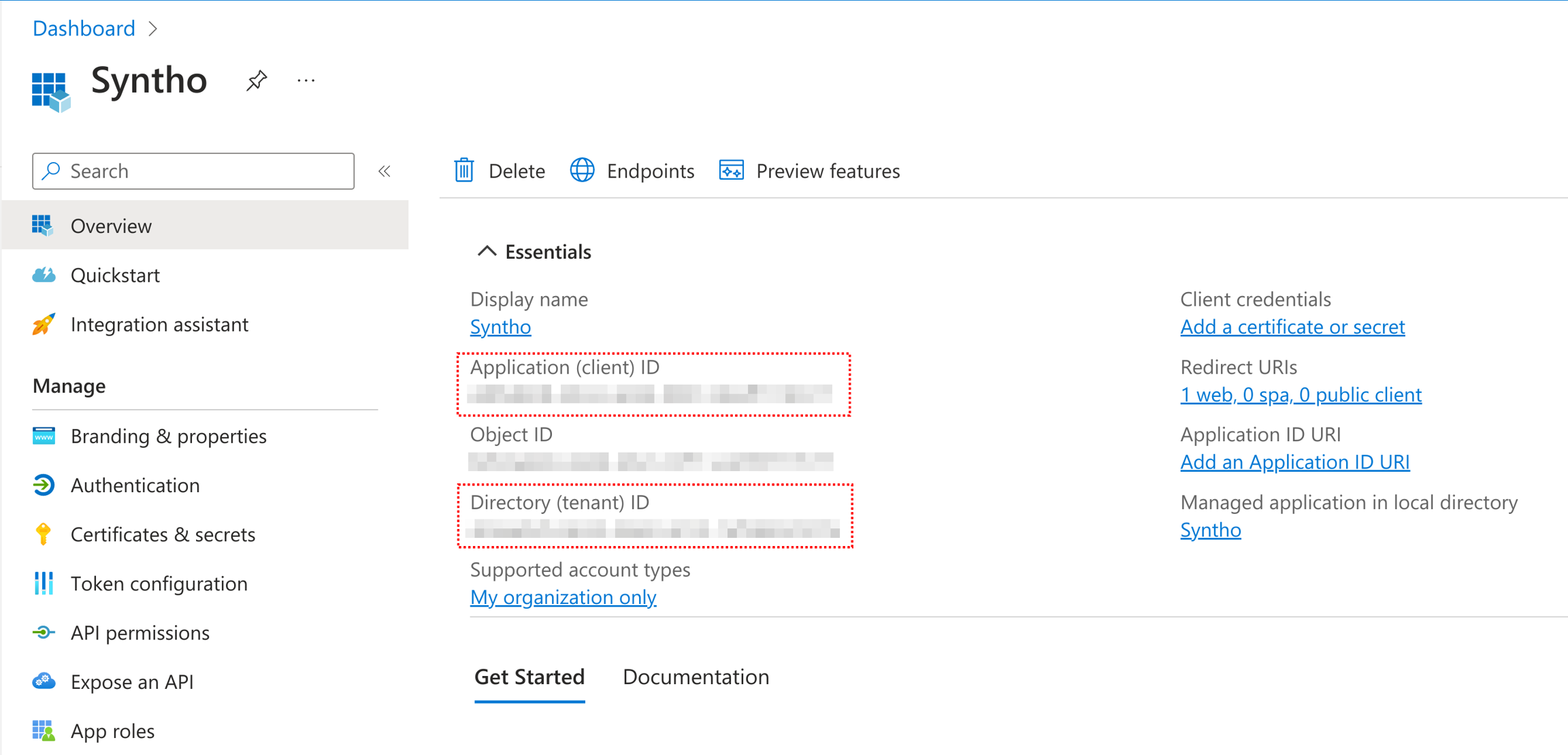
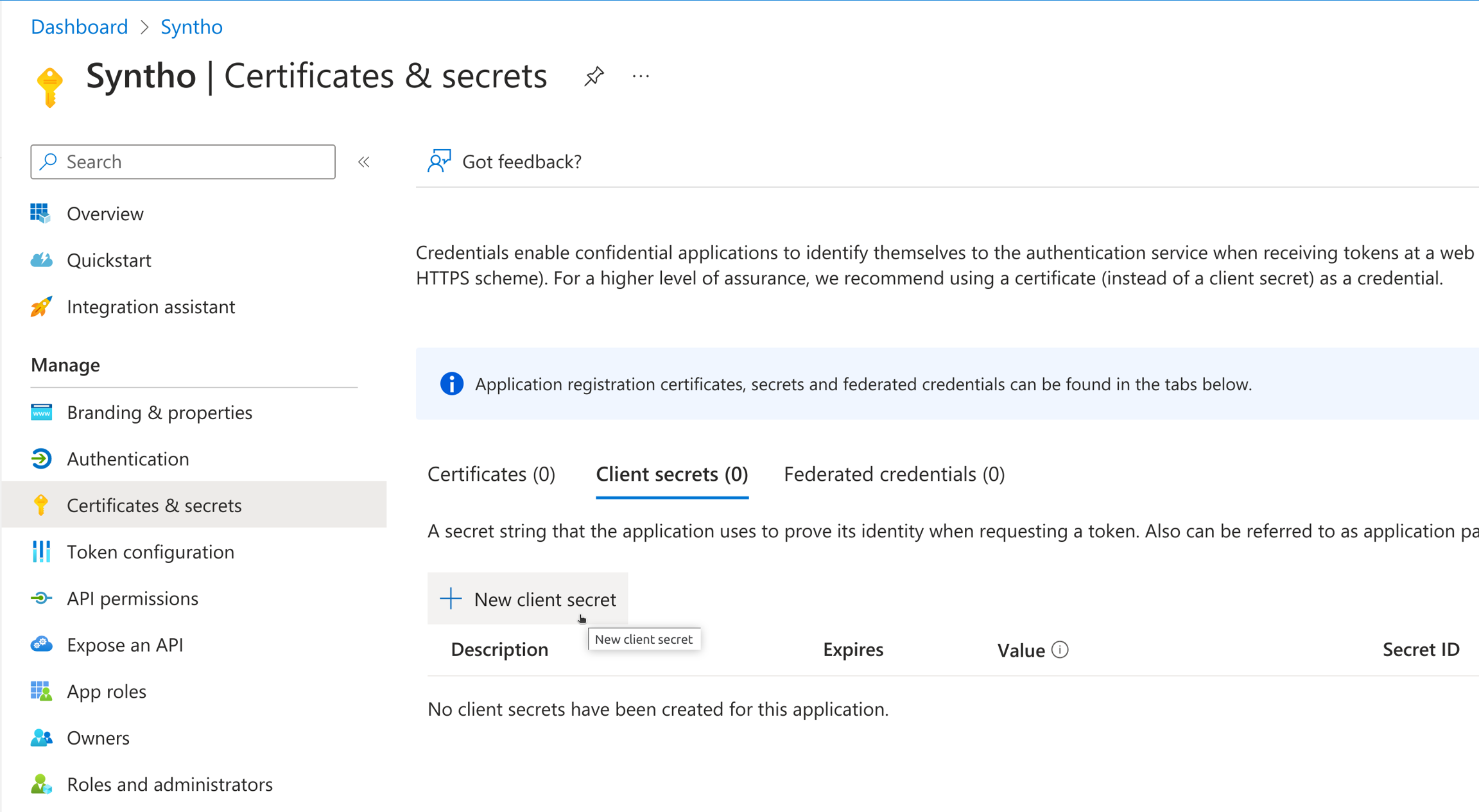
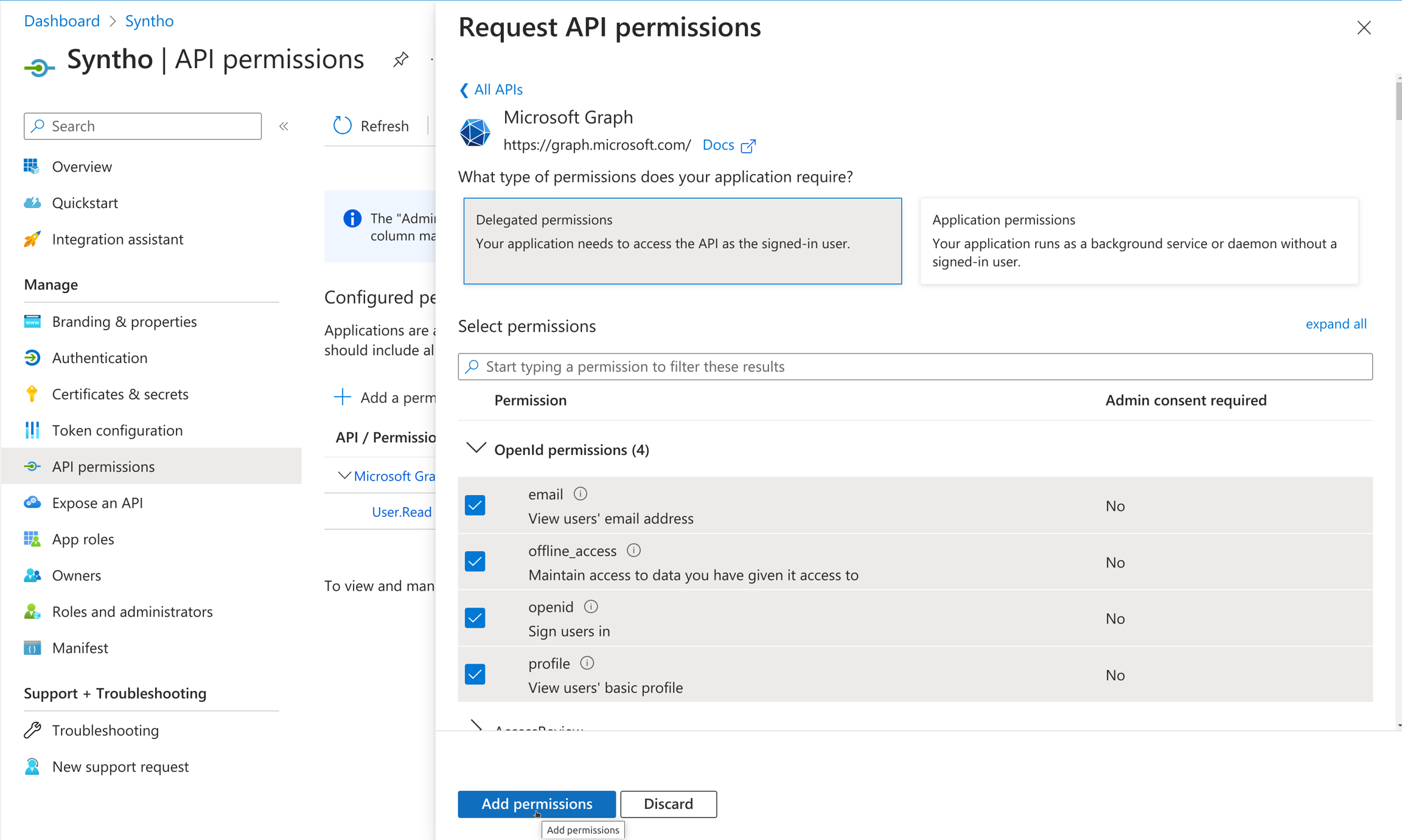
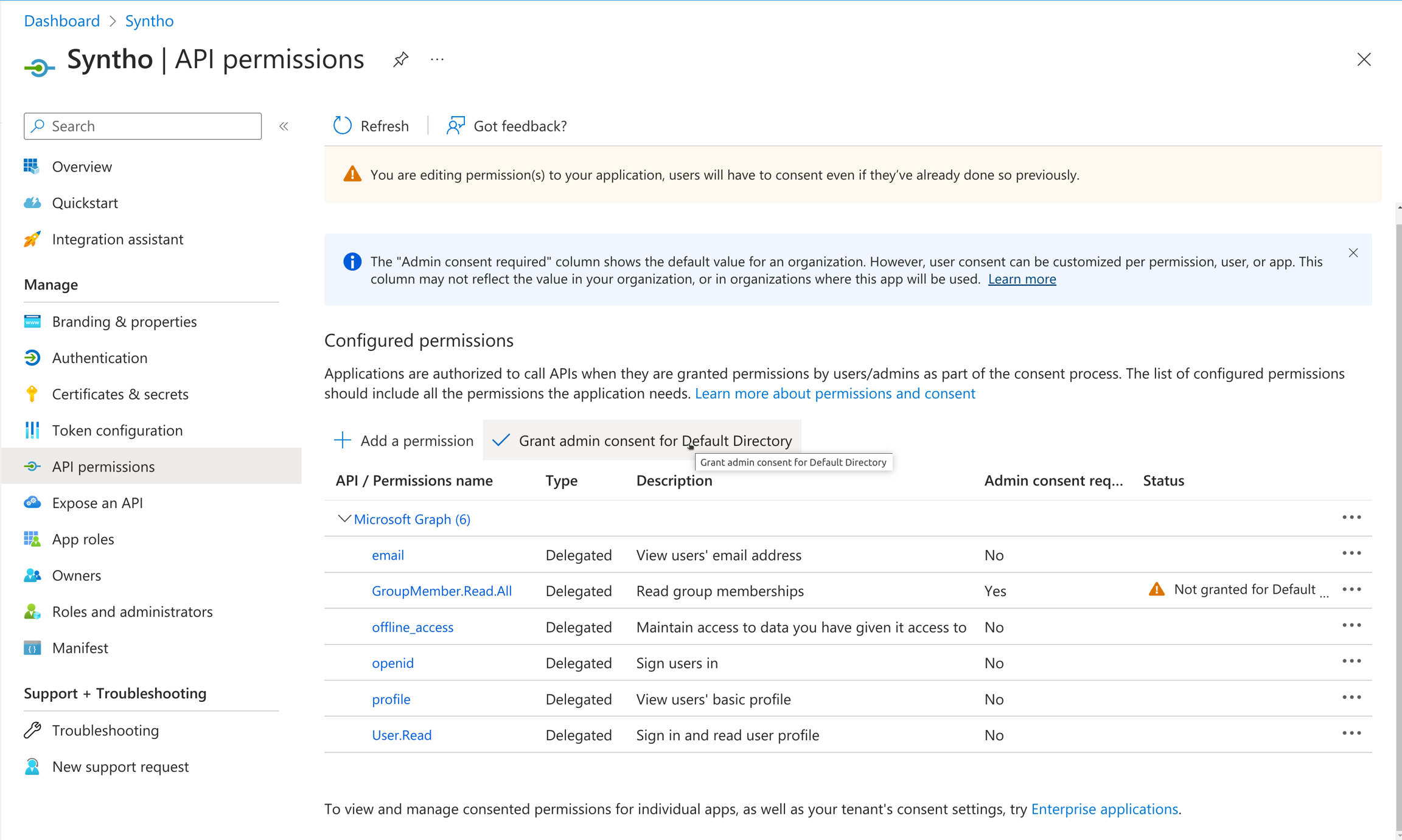
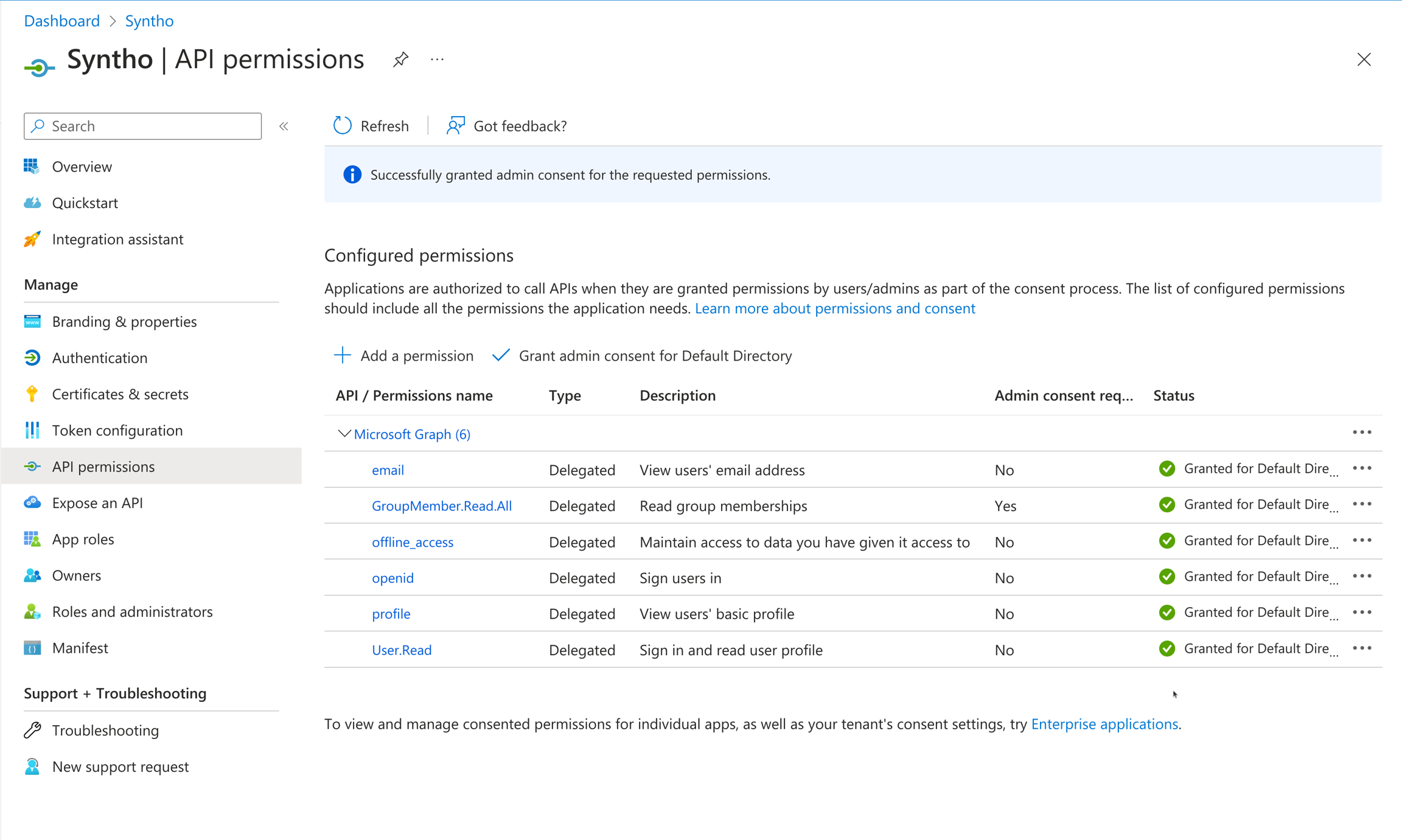
Groups
Administrator access
Limitations
Last updated
Was this helpful?

