Key generators
Syntho's Primary Key (PK) and Foreign Key (FK) generation methods are designed to enhance data privacy, integrity, and uniqueness across various tables. These methods generate unique hash values that mimic input data formats, ensuring referential integrity and maintaining the data structure.
Syntho offers three key generators to handle various scenarios for managing and transforming primary and foreign keys. Below are the descriptions and recommended use cases for Duplicate, Generate, and Hash.
Syntho supports three types of key generators to handle referential integrity:
Duplicate
Copies the original key values exactly as they appear in the source data, preserving both the correlations and referential integrity between primary and foreign keys.
When it’s essential to maintain the original key values and relationships, particularly in de-identification scenarios where the data structure must be preserved without generating new keys.
Upsampling is not supported when using Duplicate, as the original keys are simply copied, not expanded. Additionally, it is not recommended when the keys are sensitive and need to be protected, as this method retains the original key values without obfuscation.
Generate
Creates new, synthetic key values that do not correspond to the original keys. It preserves only the referential integrity, but not the correlations between key columns.
Use Generate for upsampling or creating synthetic datasets where there is no need to maintain relationships with the original data. It can also be used when creating data from scratch.
The Generate function creates new keys independently of the original key order, which disrupts correlations. As a result, it is unsuitable for scenarios where maintaining the correlations and order is essential.
Hash
Converts original key values into hashed representations. Both correlations between tables and relational integrity are maintained.
Use Hash when you need to obscure the original key values, while ensuring correlations and referential integrity are preserved.
Upsampling, or situations where the original key values must be maintained for direct referencing, such as cases where exact key values are essential for business logic (e.g. country codes) or traceability in audit scenarios.
How to apply PK / FK generators
On column level
Syntho beta feature
Go to Column settings > Generation Method, and select one of the available methods: Duplicate, Generate or Hash.
On workspace level
Setting a key column at the column level overrides the workspace's default key generation method. For example, if "Hash" is the default key generation method but "Duplicate" is set on the column level for "key_column," then "key_column" will use "Duplicate."
Use the shortcut
CTRL + SHIFT + ALT + 0to open Workspace Default Settings and change the key generation method according to your choice by simply replacing the value to either "duplicate", "generate" or "hash" . Please note that it will apply the generator across the entire workspace.Alternatively, you can add /global_settings to the end of the workspace URL to open Workspace Default Settings.
On composite keys
The generator supports composite keys and ensures consistency across all columns that form the composite key.
Setting one composite key column to use a generation method automatically sets the other composite key columns to the same method as well in UI. Attempting to change the generation method for one composite key column (e.g., from "hash" to "duplicate" or "generate") will result in all composite key columns being reset to the same generation method. The UI shows linked key generation methods, but the destination database will have the correct independent generation methods applied.
Data types
Textual data:
Hash key values ensure unique and protected data while maintaining the original text structure.
Numeric data:
Generation methods apply unique hashes to maintain numeric data privacy and integrity.
Date/Time data:
Composite keys involving date/time fields will see all parts of the composite key aligned to the same generation method when hashes are applied.
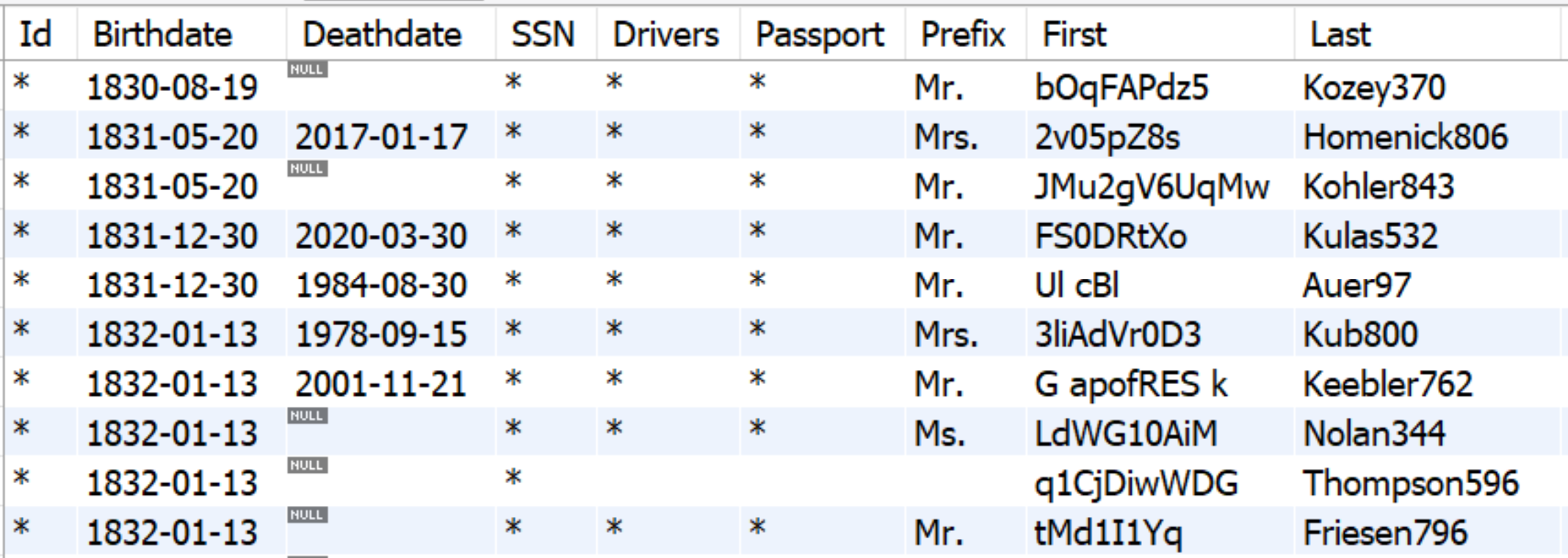
The examples below shows two different composite keys. In the first image, the columns "Birthdate" and "First" are applied "generate" and "hash", respectively.
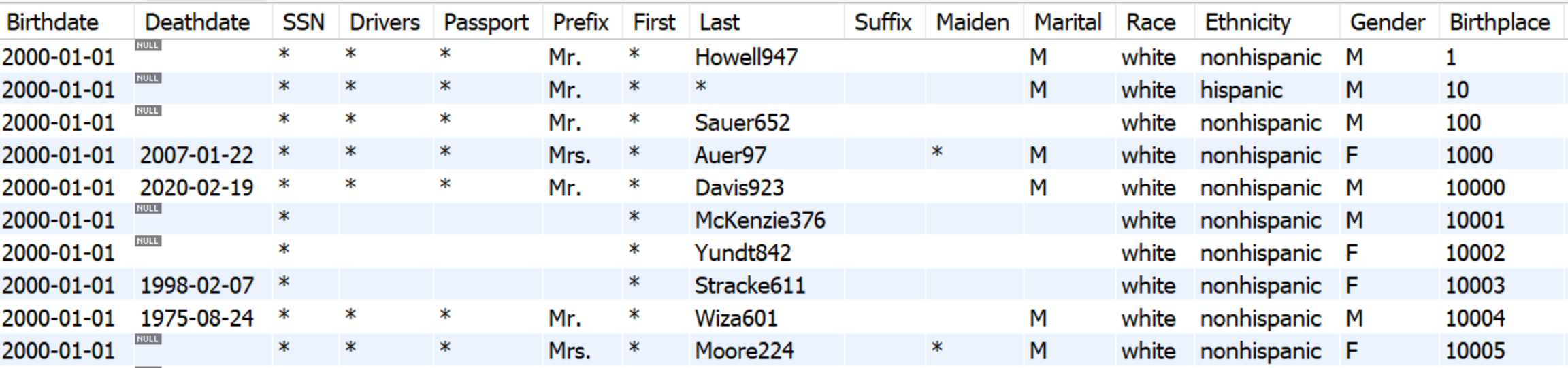
In the case below, the columns "Birthdate" and "Birthplace" are applied "hash" and "generate", respectively.
Limitations & considerations
Key generator Generate is not supported for composite foreign keys or columns referencing a composite key (i.e. unique constraint).
Generators are not applied to tables in Exclude mode.
Consistency is enabled (same input → same output) to preserve links between PK and FK columns.
Generation of keys for non-textual or highly complex data types, like images or large binary objects, is not supported.
In case you want to generate keys from scratch, set the default key generation method for you workspace to generate.
Was this helpful?

