Datetime
Below is a list of available datetime mask functions.
Hasher
The Hasher anonymizes datetime values by applying a random offset while maintaining consistency. This ensures that the relative differences between timestamps remain intact while preventing direct identification of the original values. To ensure accurate ordering, please see ordering and indexing considerations.
Parameters
No parameters.
Example
If you configure:
Column names:
1951-12-07,
1966-12-26,
1971-09-23,
...The results will be:
Column names:
1957-06-18,
1943-07-30,
2015-09-01,
...
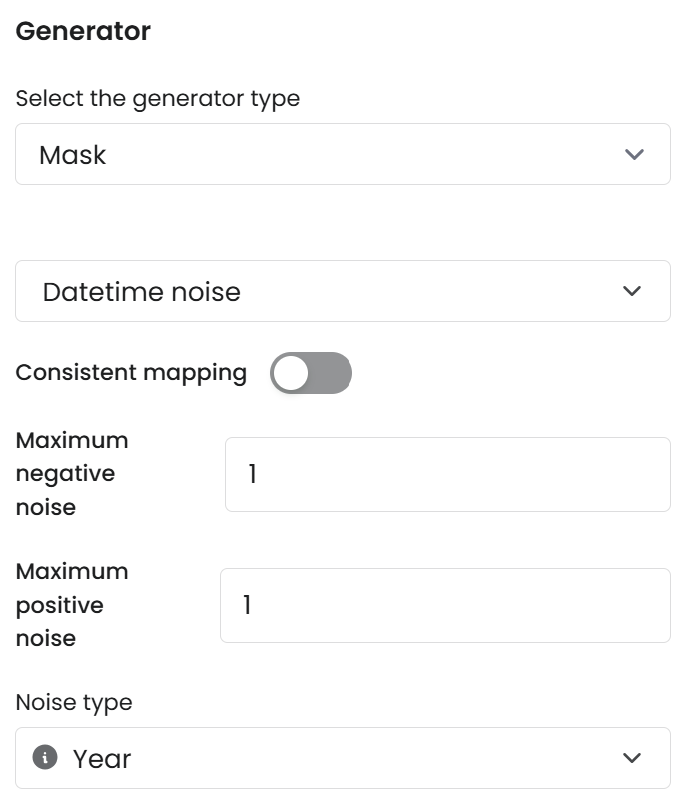
Datetime Noise
Adds a random shift to a datetime value based on specified minimum and maximum shift parameters.
Parameters
Maximum negative noise: The smallest amount the date can be adjusted, relative to the original date.Use negative numbers to shift the date into the past.
Example: If the date part is set to "Day" and the minimum shift is set to
-5, this ensures the date will not be shifted earlier than 5 days prior to the original date.A positive number shifts the date forward.
Example: If the minimum shift is
5, the date will not shift earlier than 5 days after the original date.
Maximum positive noise: The largest amount by which the date can be adjusted from the original value.Use positive numbers to shift the date into the future.
Example: If the date part is set to "Day" and the maximum shift is set to
5, the date will not be shifted later than 5 days after the original date.
Noise type: The unit of time (e.g., second, minute, hour day, month, year) that will define the granularity of the shift.The selected unit will be applied to both the minimum and maximum shift fields.
Consistent mapping: Datetime Noise supports consistent mapping.
Example
If you configure:
The results will be:
Was this helpful?

